Bioplastic materials
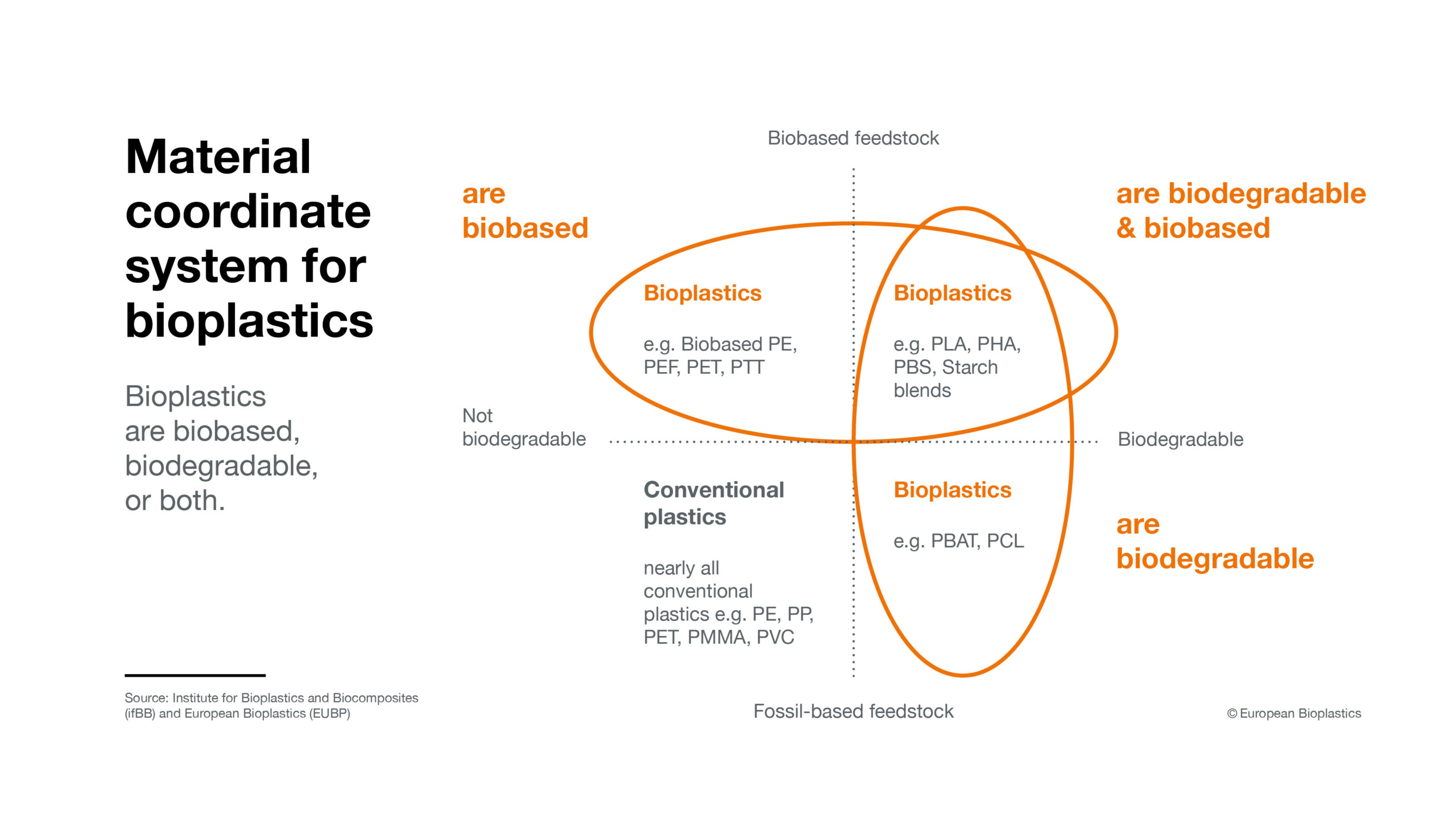
Today, there is a bioplastic alternative for almost every conventional plastic material and corresponding application. Bioplastics – plastics that are biobased, biodegradable, or both – have the same properties as conventional plastics and, in many cases, even offer additional advantages. This includes a reduced carbon footprint or additional waste management options, such as composting. Bioplastics are an essential part of the bioeconomy and a fast-growing, innovative industry that has the potential to decouple economic growth from resource depletion and environmental impact. Bioplastics are a diverse family of materials with differing properties. There are three main groups:
- Biobased or partially biobased non-biodegradable plastics, such as biobased PE, PP, or PET (so-called drop-ins) and biobased technical performance polymers, such as PTT or TPC-ET;
- Plastics that are both biobased and biodegradable, such as PLA and PHA or PBS;
- Plastics that are based on fossil resources and are biodegradable, such as PBAT.
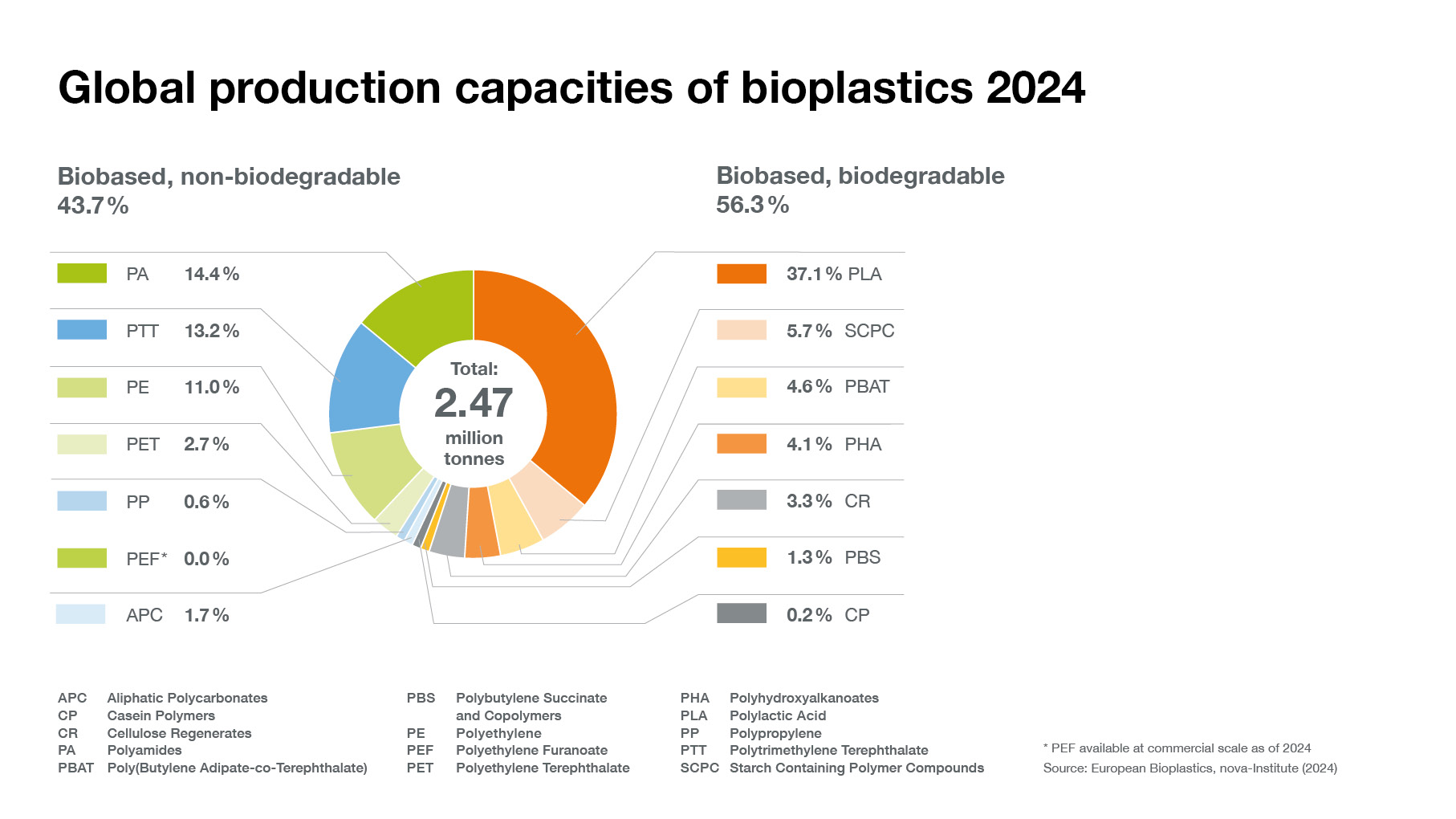
Bioplastics currently represent roughly half a percent of the almost 414 million tonnes* of plastics produced annually. But as demand is rising, and with more sophisticated materials, applications, and products emerging, the market is already growing very dynamically.
Material properties
Biobased or partially biobased durable plastics, such as biobased or partially biobased PE, PP, PET or PVC, possess properties which are identical to their conventional versions. These bioplastics are technically equivalent to their fossil counterparts; yet they help to reduce a product’s carbon footprint. Moreover, they can be mechanically recycled in existing recycling streams.
Find out more about biobased plastics here.
Additionally, new materials, such as PLA, PHA, cellulose or starch-based materials offer solutions with completely new functionalities, such as compostability and in some cases optimised barrier properties. Find out more about biodegradable plastics here. Along with the growth in variety of bioplastic materials, properties, such as flexibility, durability, printability, transparency, barrier, heat resistance, gloss and many more have been significantly enhanced.
Accurate claims and labels ensure clarity and trust: Environmental claims of bioplastics materials and products, such as biodegradability and the amount of biomass content, must always be specific, accurate, and ideally provide a third-party substantiation for these claims. A label awarded in accordance with independent certification based on acknowledged standards guarantees that the product fulfils the criteria claimed. As non-experts cannot distinguish bioplastics from conventional plastics, reliable certification and labelling based on approved standards provided by CEN, ASTM, or ISO help the consumer to identify these products and receive information about additional qualities the material or product possesses.
*Source: World plastics production 2023, Plastics Europe, 2024.