Bioplastics market development update 2024
Continuous growth: global production capacities of bioplastics 2024-2029
Bioplastics currently represent roughly half a percent of the almost 414 million tonnes* of plastics produced annually.
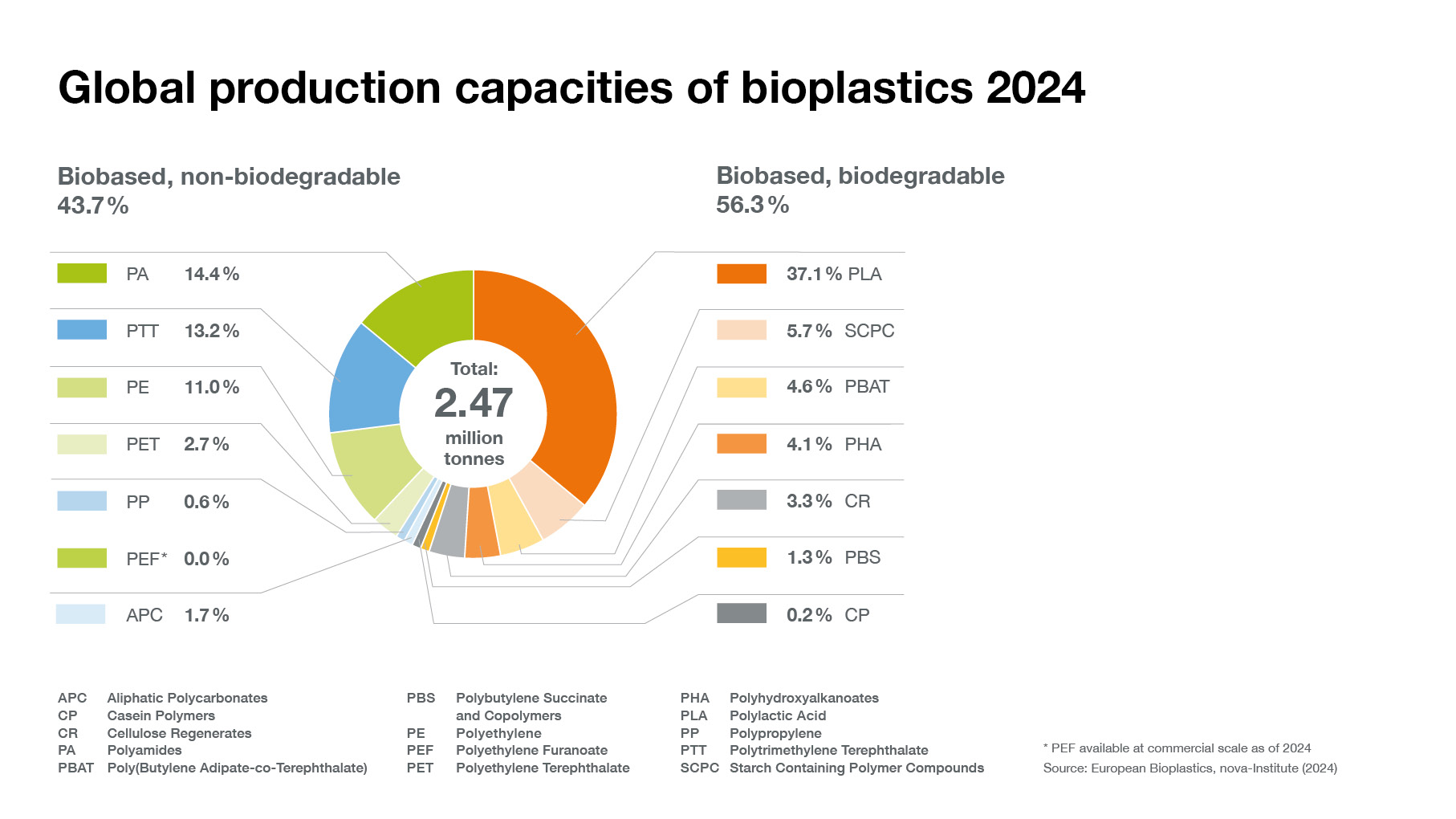
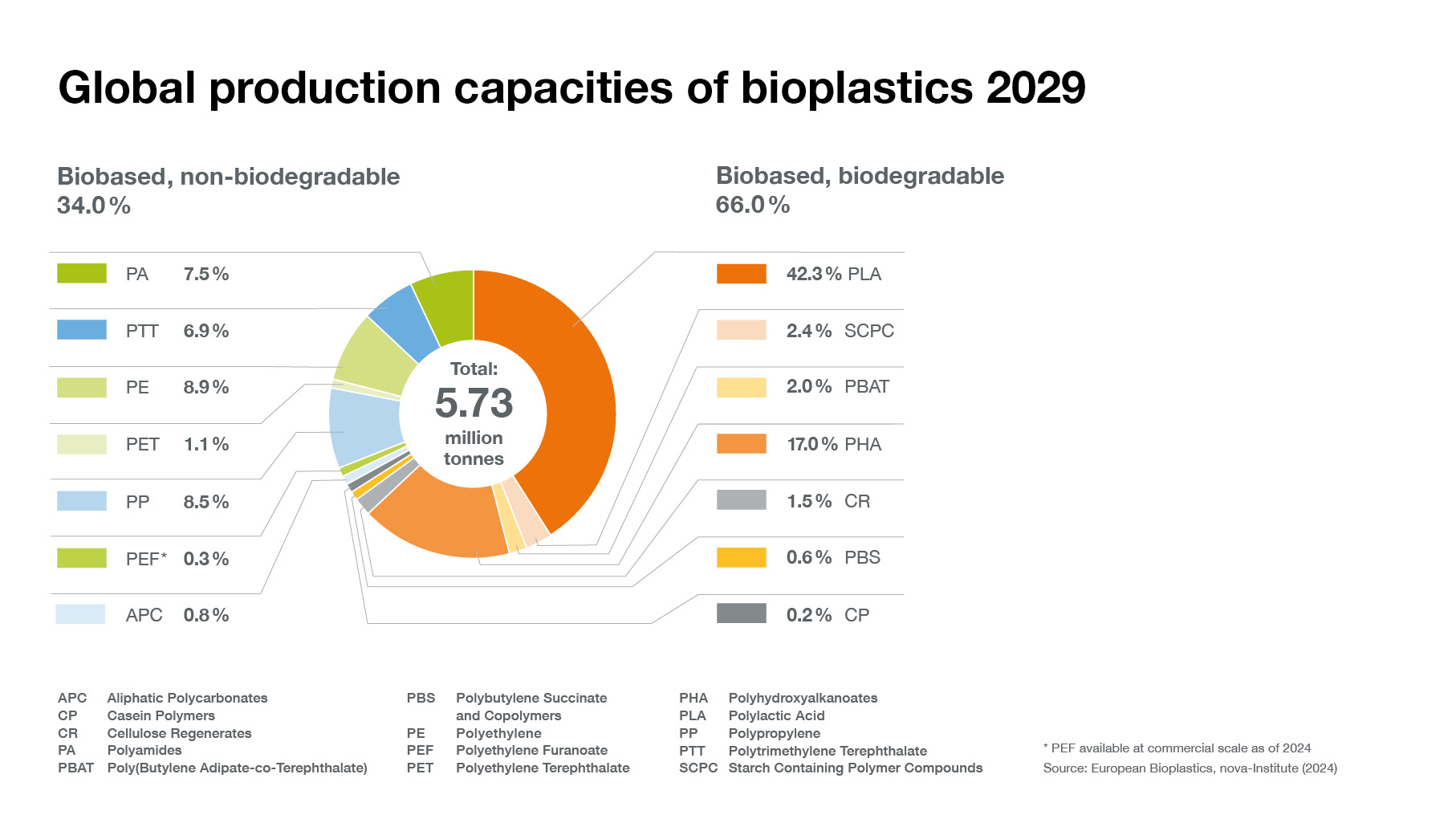
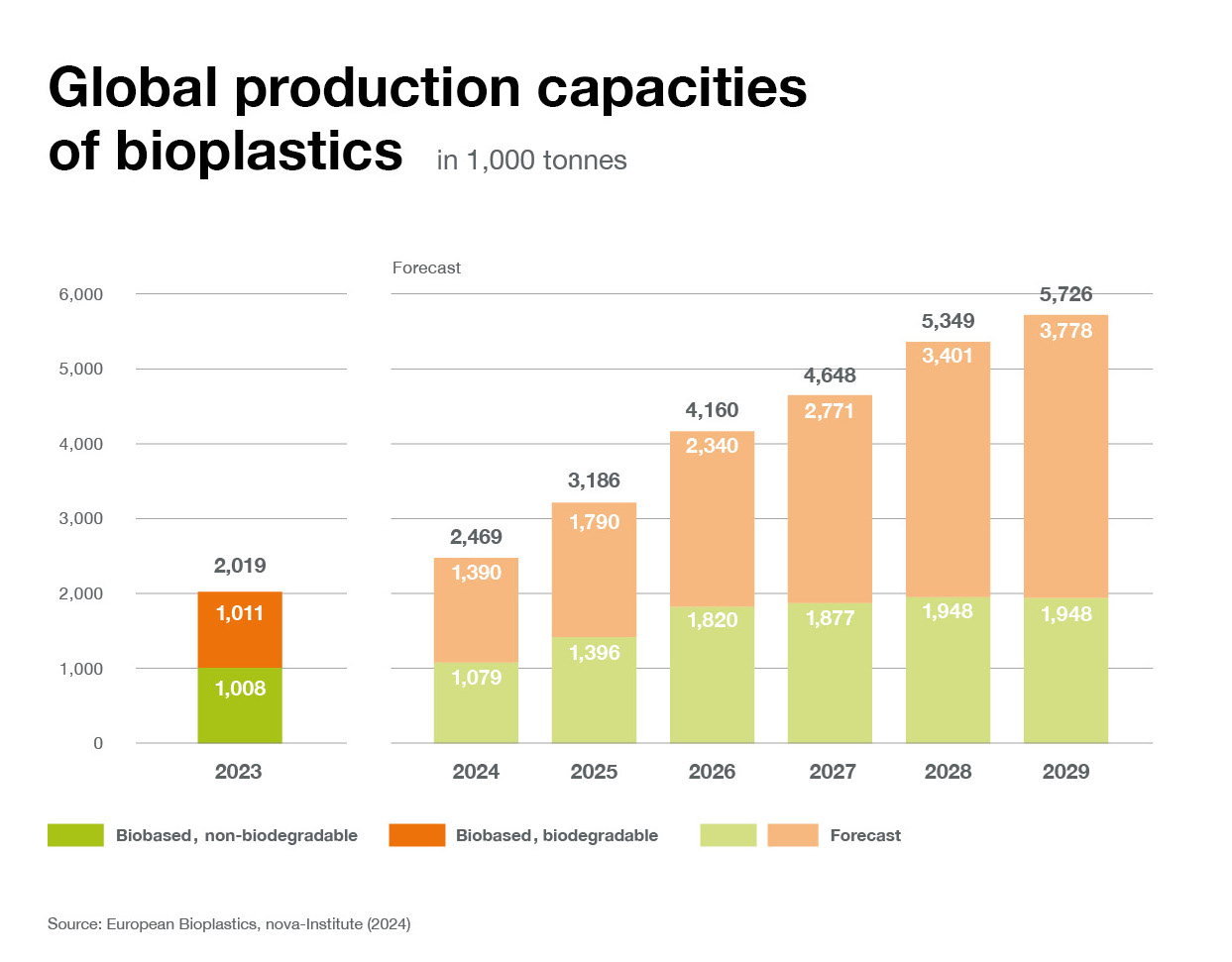
Overall global plastics production continues to rise steadily. This development is driven by rising demand combined with the emergence of ever more sophisticated applications and products. In line, global bioplastics production capacity is set to increase significantly from around 2.47 million tonnes in 2024 to approximately 5.73 million tonnes in 2029.
Material development and diversification
Bioplastic alternatives exist for almost every conventional plastic material and corresponding application. Due to a strong development of biobased and biodegradable polymers, such as polylactic acid (PLA) and polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA), biobased polyethylene (PE) as well as a steady growth of biobased polypropylene (PP), the production capacities will continue to increase significantly within the next 5 years.
Applications and market segments
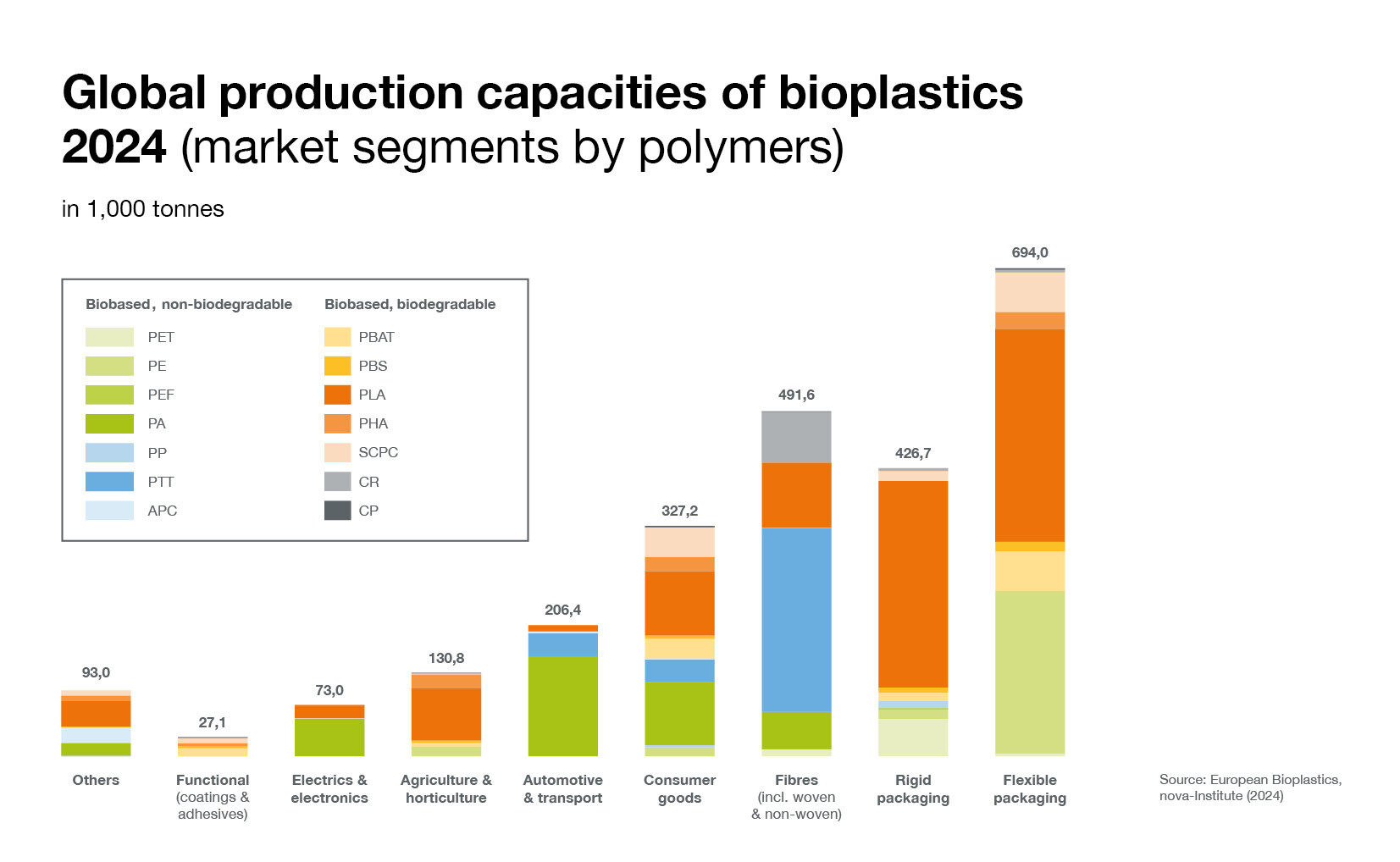
Bioplastics are used for an increasing variety of applications, ranging from packaging and fibres to consumer goods, automotive, and agricultural products. Packaging remains the largest market segment for bioplastics with 45 percent (1.12 million tonnes) of the total bioplastics market in 2024.
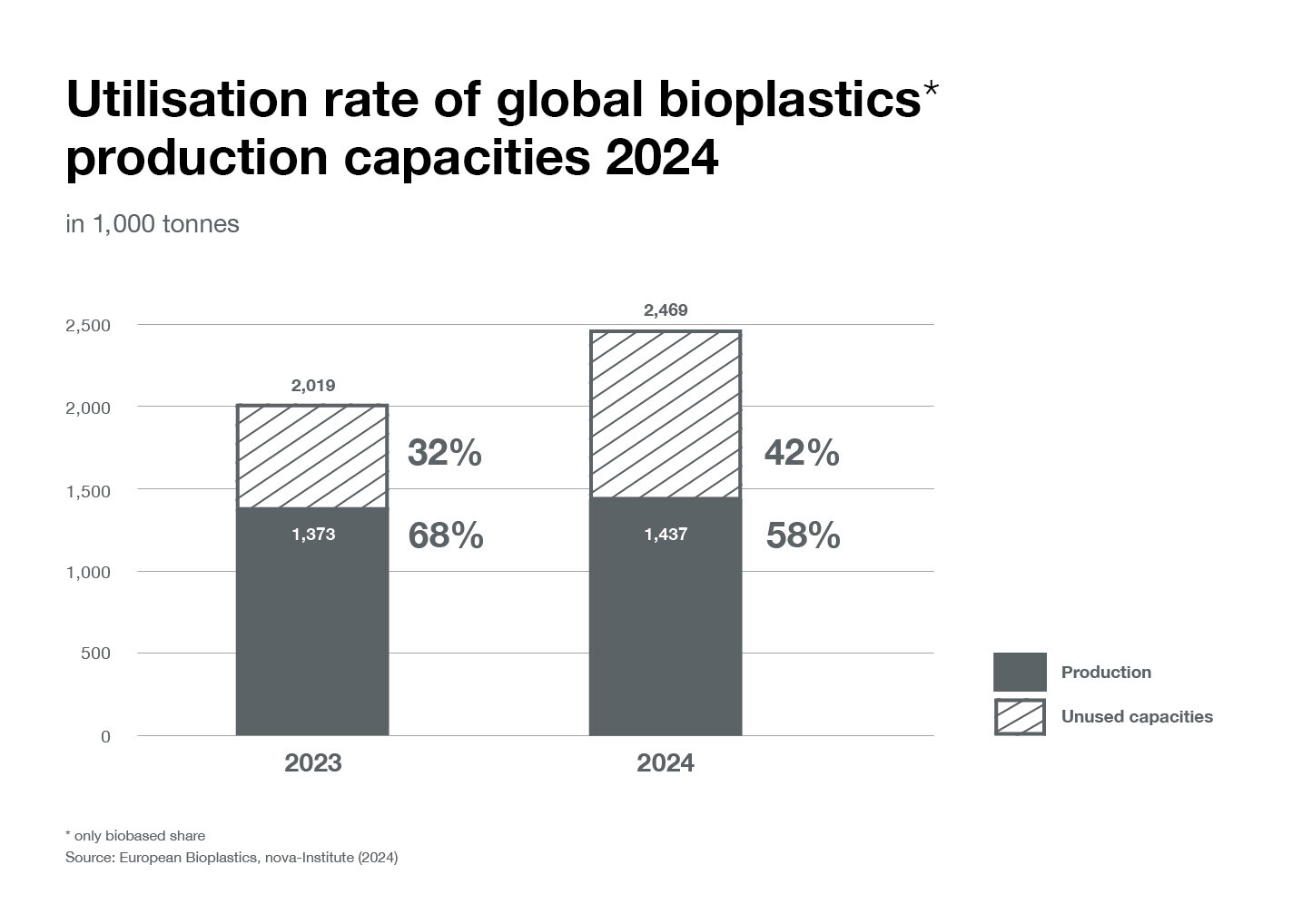
Bioplastics production at close to 60% capacity in 2024
The comparison between the production capacities and actual production in 2024 shows that the bioplastics industry is producing at almost 60% capacity. Although varying in some parts quite significantly from one polymer to another, ranging from 35% to 100%, the average utilization rate in 2024 is 58% (1.44 million tonnes production vs. 2.47 million tonnes production capacities).
About this market data update
The market data update 2024 has been compiled in cooperation with the market experts of the nova-Institute (Hürth, Germany).
The market data graphs are available for download on http://www.european-bioplastics.org/news/publications/
*World plastics production 2023, Plastics Europe, 2024.