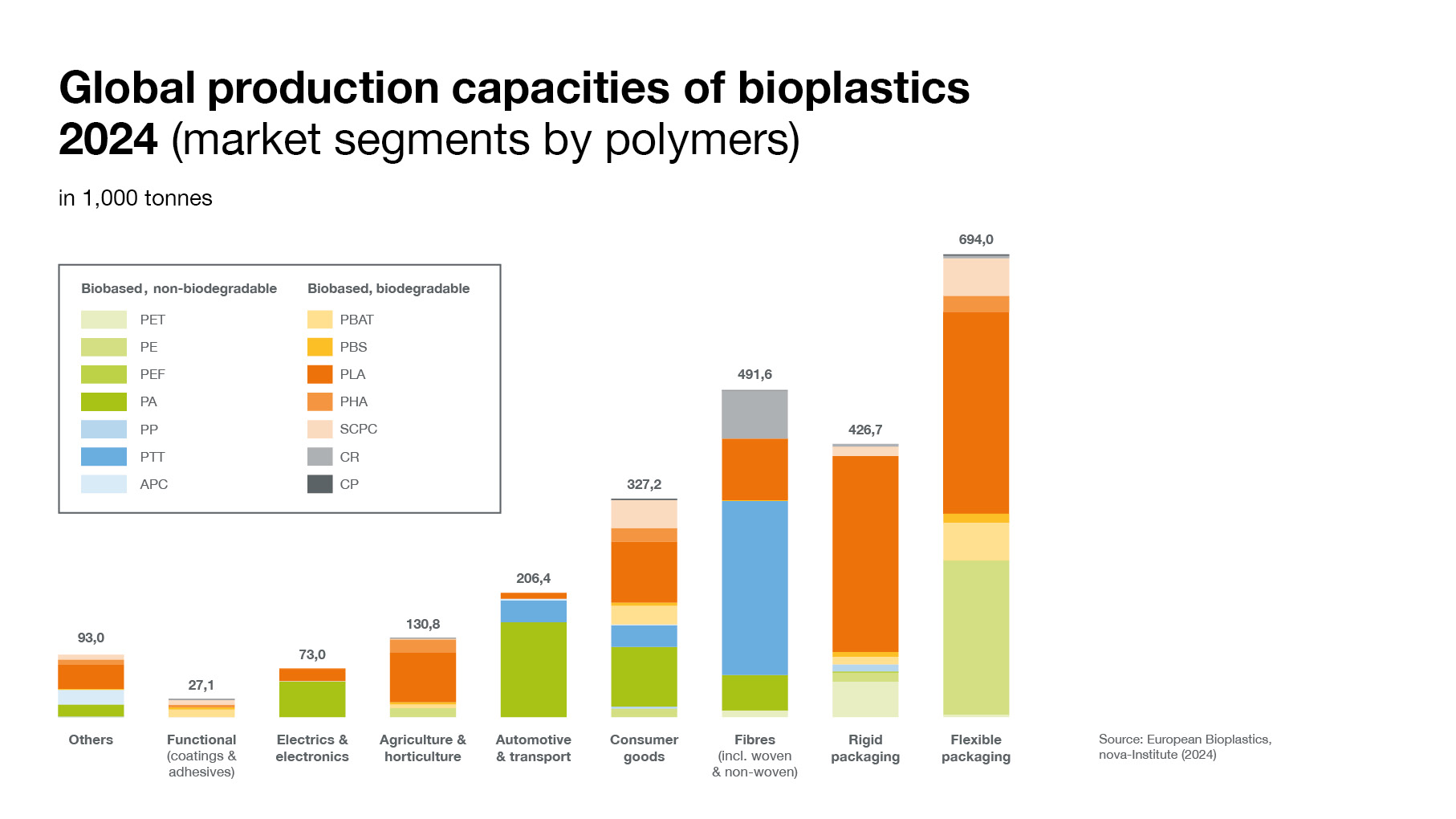
Market drivers and development
Today, there is a bioplastic alternative for almost every conventional plastic material and corresponding application. Bioplastics have the same properties as conventional plastics and offer additional advantages, such as a reduced carbon footprint or additional waste management options, such as composting. The current market for bioplastics is characterised by a dynamic growth rate and a strong diversification. There is a multitude of applications for bioplastics ranging from beverage bottles in the packaging segment to keyboards in the consumer electronics segment and interior parts in the automotive sector.
With a growing number of materials, applications, and products, the number of manufacturers, converters, and end-users also increases steadily. Significant financial investments have been made into production and marketing to guide and accompany this development.
The latest market data does not only demonstrate the contributions of the industry on moving towards a sustainable future with a reduced environmental impact. The forecast also predicts the budding bioplastics industry to unfold an immense economic potential over the coming decades.
The factors driving market development are both internal and external. External factors make bioplastics the attractive choice. This is reflected in the high rate of consumer acceptance. Moreover, the extensively publicised effects of climate change, price increases of fossil materials, and the increasing dependence on fossil resources also contribute to bioplastics being viewed favourably.
From an internal perspective, bioplastics are efficient and technologically mature materials. They are able to improve the balance between the environmental benefits and the environmental impact of plastics. Life cycle analyses demonstrate that bioplastics can significantly reduce CO2 emissions compared to conventional plastics (depending on the material and application). Furthermore, the increasing utilisation of biomass in bioplastic applications has two clear advantages: renewability and availability.
European Bioplastics focuses and promotes its activities on European and Member States’ level. Numerous countries outside the European Union are actively pursuing the development of bioplastics. Europe in particular offers excellent general conditions to compete globally for future markets and technologies. These include:
- A highly developed economy and educated society
- Leading global companies in the chemical and plastics industries
- Industrial users with the aim of promoting sustainable development
- Consumers with strong purchasing power and a high degree of environmental awareness
Political support
It is essential for the further development of the market that products are marketed profitably even at this early stage. A secure investment framework and support from policy makers will foster the framework needed to nurture this pillar of a sustainable future. In this regard, the European Commission adopted a policy framework for biobased, biodegradable and compostable plastic.
Several policy processes, many of them related to the European Green Deal have the potential to boost the role of bioplastics in developing a truly circular bioeconomy, enabling innovation, and attracting new investments. In recent years, the European Union has made increasing efforts to introduce or adapt policies, regulatory frameworks, and standards to strengthen and implement the bioeconomy and circular economy in Europe, all of which affect the bioplastics sector in one way or other.
Research on the biobased economy is already supported by several national governments as well as by various EU programmes, in the past by “Horizon 2020” and now by its successor “Horizon Europe”. Horizon Europe, which will run from 2021 to 2027, enables a significant increase in funding for bio-economic research. European Bioplastics supports all efforts to strengthen R&D activities in Europe. However, in other areas, EU entities still display a rather critical view on bioplastics, which often diminishes the investment that has been made in the research field. Thus, EUBP welcomes any measures that facilitate the market introduction of bioplastics.
A common label for Europe
Association members have made a voluntary commitment to certify and label their industrially compostable products according to the EU standard EN 13432 / EN 14995 if they wish to advertise “compostable” properties. In addition, the European Committee for Standardization (CEN) has published the standards EN 16640 and EN 16785-1 on the subject of the “biobased” element of bioplastics. The standard EN 16640 “Biobased products – Determination of the biobased carbon content of products using the radiocarbon method“, published in 2017, describes how to measure the carbon isotope 14C (radiocarbon method). Depending on the amount of biobased carbon measured, certification will be carried out. In addition, the standard EN 16785-1 “Biobased products – Biobased content – Part 1: Determination of the biobased content using the radiocarbon analysis and elemental analysis“ has been developed to also account for other biobased elements in a polymer through elemental analysis. The “OK biobased” certification system by TÜV Austria, the “DIN geprüft biobased” by DIN Certco as well as the “NEN biobased” are relevant labels that verify the material composition of a product according to those EN standards.
Consumer behaviour
According to the last Eurobarometer Survey conducted by the European Commission (2023), about 73 percent of European customers want to buy products with a minimal impact on the environment. The fact that biobased plastics display clear advantages over conventional plastics makes them attractive to the environmentally conscious customers. This of course means that the use of biobased plastics needs to be explained and marketed transparently: How much biobased content is in the packaging? How much CO2 emissions are saved? And was the biomass grown sustainably? These are questions that need to be answered.
Big brands adopt bioplastics for prominent consumer products
With an ever-growing number of big brands turning to bioplastic solutions, the market penetration is well on its way. Brands and brand owners, such as Tetra Pak, Danone, Procter & Gamble, Puma, Lego, IKEA, Heinz, or Toyota have already introduced first large scale products in Europe.
The introduction of different bioplastic materials with these new products will raise the level of awareness and information significantly. The quality of the materials will become apparent and accepted. And with increasing volumes of bioplastics on the market, currently higher production cost will gradually converge to those for conventional materials.